Federal Photo-Matching Scheme Detects Passport Fraud
The Federal Government’s New Weapon Against Passport Fraud: Facial Recognition Technology
In today’s technology-driven world, governments leverage advanced tools to enhance security and combat fraud. The Canadian federal government has unveiled a new weapon to tackle passport fraud: a sophisticated facial recognition system.
This system has already identified 15 individuals using fraudulent identities this year alone. This initiative marks a significant step forward in Canadian authorities’ use of biometrics, including fingerprints, images, and iris scans.
These tools have proven effective in tracking down criminals with immigration warrants or links to terrorism, organized crime, and human rights violations. With growing evidence of its success, there is speculation that the Liberal government might make this facial recognition scheme permanent. This would further strengthen Canada’s border security.
The Growing Role of Biometrics in Security
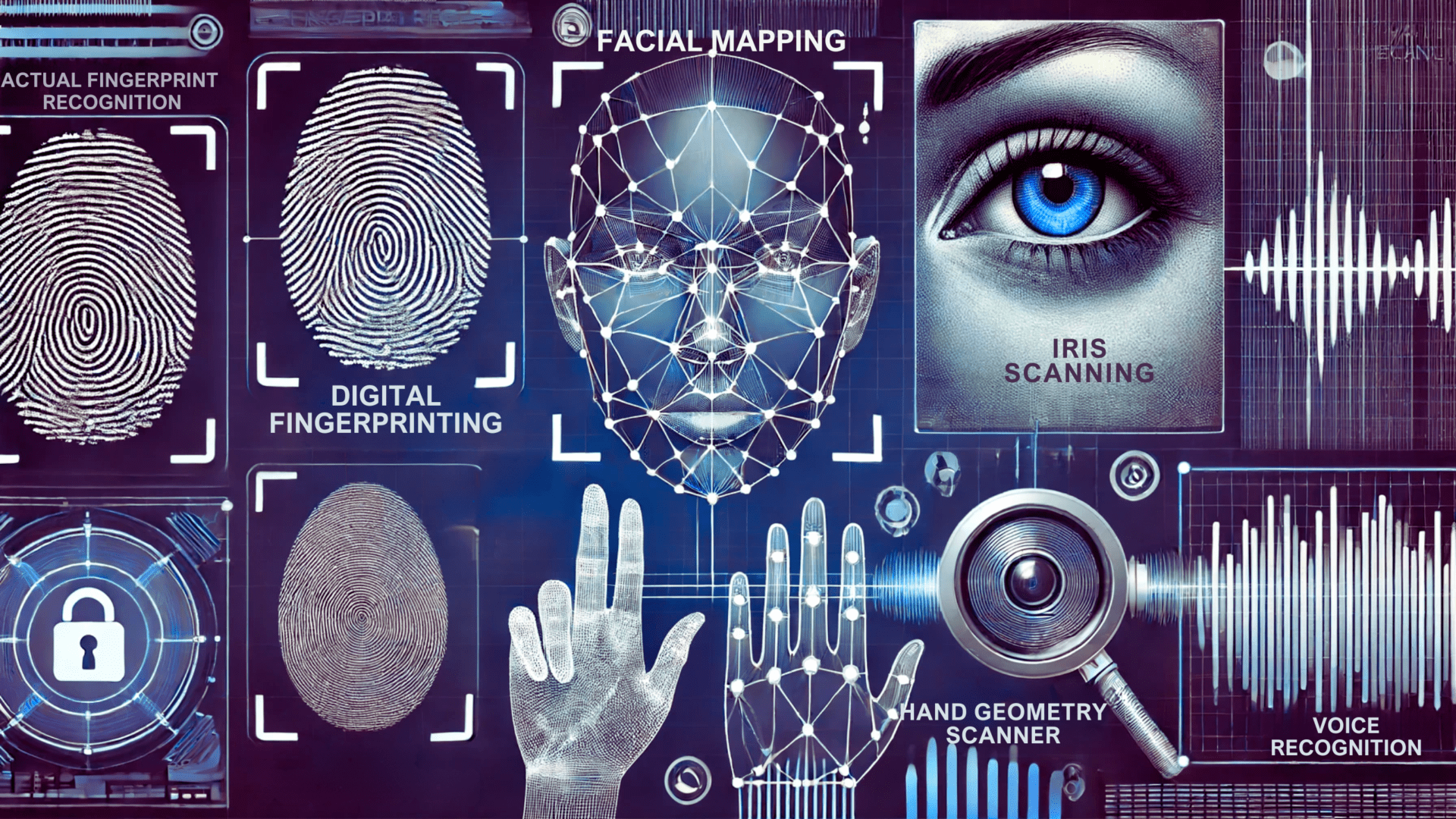
Biometrics, the science of analyzing physical or behavioural characteristics to verify identity, has become indispensable in modern security systems.
Fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans are now common in various sectors, from law enforcement to banking. For Canadian authorities, these technologies offer a robust solution to the persistent problem of identity fraud.
Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology analyzes a person’s unique features, such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the cheekbones, and the contour of the lips. This data is then compared against a database of known images to verify identity.
In recent years, Canada has increasingly relied on biometrics to enhance its security measures. The facial recognition system’s ability to identify 15 individuals with fraudulent identities demonstrates its potential.
This success builds on earlier uses of biometrics, which have helped Canadian authorities track down criminals involved in terrorism, organized crime, and human rights violations.
The Origins of the Initiative
Internal memos, released under the Access to Information Act, reveal that the photo-matching system idea stemmed from concerns within the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA).
Officials worried that individuals wanted by the CBSA might use false identities to obtain genuine Canadian travel documents from the Immigration Department’s passport program.
A memorandum of understanding between the CBSA and immigration agencies highlights the value of real Canadian passports to those seeking to create fake identities. It states, “People with outstanding immigration arrest warrants can hide from law enforcement by travelling or living in communities under fake names while still getting benefits and services.”
Pilot Projects and Results
Initial tests of the facial recognition system were encouraging, leading to a 2014 pilot project. During this pilot, the border agency shared photos and biographical information of 1,000 wanted individuals flagged as high-risk. They wanted to check if these individuals had applied for or obtained Canadian travel documents under false identities.
Successes of the Pilot Project
The results were promising. The system identified 15 matches, prompting “appropriate enforcement action” from the agency. This could include criminal charges, revocation of citizenship, or further investigation by the border agency to locate the wanted individuals.
In cases where the whereabouts of these individuals were unknown, the agency could issue a border “lookout” to monitor their movements.
Esme Bailey, a spokeswoman for the CBSA, noted that no further details could be released to avoid compromising ongoing investigations. However, she confirmed that a second phase of the pilot project had been approved and completed by the end of March. The data from this phase is still being analyzed. Once the analysis is complete, more statistics will be available.
Privacy Concerns and Measures
Implementing facial recognition technology raises privacy concerns. To address these, the CBSA and immigration officials completed a privacy questionnaire for the pilot phase.
If the project moves forward, a full privacy impact assessment will be conducted to ensure that personal information is not misused. Bailey mentioned that while the privacy commissioner’s office had not been consulted on the project, the CBSA and the passport program had informed the commissioner about other facial recognition initiatives. This proactive communication aims to maintain transparency and uphold privacy standards.
How Facial Recognition Technology Works
Understanding how facial recognition technology works can shed light on its effectiveness and the challenges it may face. Here’s a deeper look into the mechanics behind this advanced technology:
Image Capture
The first step involves capturing a high-quality image of an individual’s face. Cameras at border checkpoints, passport application centers, or other government offices can do this.
Feature Extraction
The system analyzes the captured image. It identifies critical facial features such as the distance between the eyes, the nose’s width, the cheekbones’ shape, the lips’ contour, and the eye sockets’ depth. These features are converted into a mathematical representation known as a facial signature.
Comparison
The facial signature is compared against a database of stored images. This database may include photos from previous passport applications, visa applications, criminal records, and government-issued IDs.
Matching
The system uses algorithms to find matches between the captured image and the database. The system flags the individual for further investigation if a match is found.
Advantages of Facial Recognition Technology
The use of facial recognition technology offers several advantages, particularly in the context of border security and fraud prevention:
High Accuracy
Advanced algorithms and high-quality image capture ensure that the system can accurately identify individuals, even if they attempt to alter their appearance.
Speed and Efficiency
Automated matching processes allow for quick identification, reducing the time and resources needed for manual checks.
Deterrent Effect
Knowing that advanced biometric systems are in place may deter individuals from attempting to use false identities or commit fraud.
Integration with Other Systems
Facial recognition can be integrated with other security systems, such as fingerprint and iris recognition, to provide a comprehensive approach to identity verification.
Challenges and Limitations
While facial recognition technology offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges and limitations that must be addressed:
Privacy Concerns
Using biometric data raises concerns about privacy and the potential for misuse of personal information. Ensuring robust data protection measures is crucial.
False Positives and Negatives
No system is infallible. False positives (incorrectly identifying a person as someone else) and false negatives (failing to recognize someone) can occur, leading to potential inconveniences and security gaps.
Technical Issues
Factors such as poor lighting, low-quality images, and changes in physical appearance (e.g., aging and facial hair) can affect the system’s accuracy.
Ethical Considerations
Facial recognition technology must be implemented carefully, considering ethical implications, including potential bias and discrimination.
Implications for Border Security
The permanent implementation of facial recognition technology could significantly enhance Canada’s ability to secure its borders and prevent individuals with fraudulent identities from entering the country. Biometrics could create substantial barriers for those attempting to slip through undetected.
Increased Security
Enhanced verification processes make it difficult for criminals and individuals with outstanding warrants to use false identities.
Efficient Identification
Rapid identification of fraudulent documents can streamline immigration processes and reduce the burden on border security personnel.
Deterrent Effect
The knowledge that advanced biometric systems are in place may deter individuals from attempting to use fake identities.
Future Prospects
As biometric technology evolves, its border security and identity verification applications will likely expand. The Canadian government’s pilot projects and ongoing analysis suggest a commitment to leveraging these technologies to enhance national security.
The potential for permanent implementation of facial recognition systems indicates a forward-thinking approach to tackling identity fraud. By integrating these technologies into standard procedures, Canada could set a precedent for other nations seeking to improve their border security.
Conclusion
The federal government’s introduction of facial recognition technology to combat passport fraud significantly advances Canada’s security measures. This innovative tool has already demonstrated its effectiveness in identifying individuals with fraudulent identities, contributing to the broader effort to enhance border security and track down criminals.
As Canada considers making this system permanent, balancing the benefits of increased security with the need to protect individual privacy is crucial. By conducting thorough privacy impact assessments and maintaining transparency with the public, Canadian authorities can ensure that the use of biometrics aligns with ethical standards and legal requirements.
For those interested in learning more about the implications of biometric security measures or seeking guidance on related matters, contacting professionals at Amicus International Consulting can provide valuable insights and assistance.
If you want to work with a professional team to help you transition to a life of freedom, contact Amicus Int. for New Identity services today.
If you would like to work with a professional team that can help make your transition to a life of freedom, contact Amicus Int. for New Identity services today.